Conversion between Representations of Responses or States
conversion.RdConverts between binary matrix and pattern representations of response patterns or knowledge states.
as.pattern(R, freq = FALSE, useNames = FALSE, as.set = FALSE,
sep = "", emptyset = "{}", as.letters = NULL)
as.binmat(N.R, uniq = TRUE, col.names = NULL, as.logical = FALSE)
is.subset(R)Arguments
- R
an indicator matrix of response patterns or knowledge states.
- N.R
either a (named) vector of absolute frequencies of response patterns; or a character vector of response patterns or knowledge states; or a
setof sets representing the knowledge structure.- freq
logical, should the frequencies of response patterns be reported?
- uniq
logical, if
TRUE, only the unique response patterns are returned.- useNames
logical, return response patterns as combinations of item names.
- as.set
logical, return response patterns as set of sets.
- sep
character to separate the item names.
- emptyset
string representing the empty set if
useNamesisTRUE.- as.letters
deprecated, use
useNamesinstead.- col.names
column names for the state or response matrix.
- as.logical
logical, return logical matrix of states.
Value
as.pattern returns a vector of integers named by the response
patterns if freq is TRUE, else a character vector. If
as.set is TRUE, the return value is of class set.
as.binmat returns an indicator matrix. If as.logical is
TRUE, it returns a logical matrix.
is.subset returns a logical incidence matrix of the subset relation
among states.
See also
blim, set in package sets.
Examples
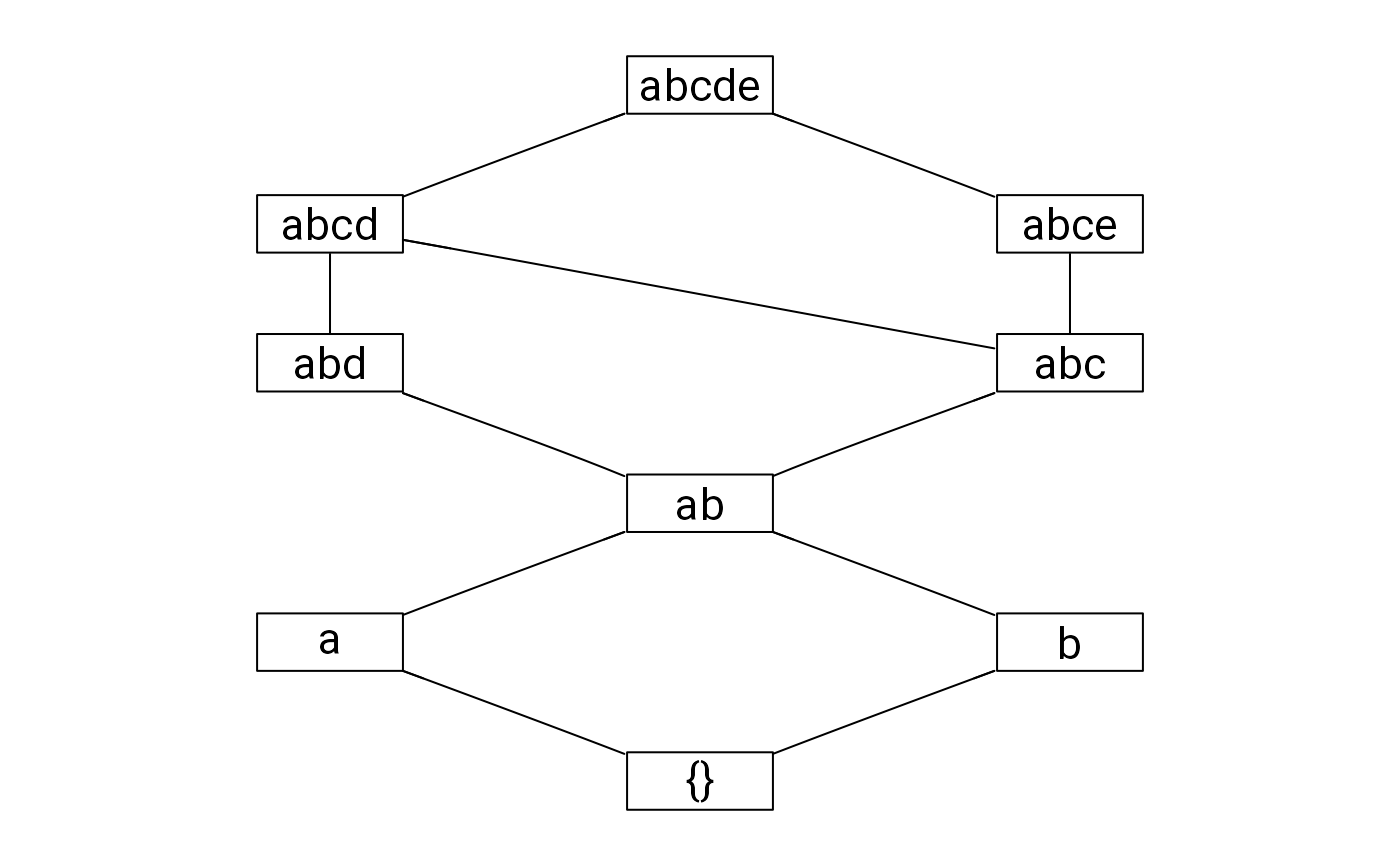
data(DoignonFalmagne7)
K <- DoignonFalmagne7$K
as.pattern(K, freq = TRUE)
#> 00000 01000 10000 11000 11010 11100 11101 11110 11111
#> 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
as.pattern(K)
#> [1] "00000" "10000" "01000" "11000" "11100" "11010" "11110" "11101" "11111"
as.pattern(K, useNames = TRUE)
#> [1] "{}" "a" "b" "ab" "abc" "abd" "abcd" "abce" "abcde"
as.pattern(K, as.set = TRUE)
#> {{}, {"a"}, {"b"}, {"a", "b"}, {"a", "b", "c"}, {"a", "b", "d"}, {"a",
#> "b", "c", "d"}, {"a", "b", "c", "e"}, {"a", "b", "c", "d", "e"}}
N.R <- DoignonFalmagne7$N.R
dim(as.binmat(N.R))
#> [1] 32 5
dim(as.binmat(N.R, uniq = FALSE))
#> [1] 1000 5
## Knowledge structure as binary matrix
as.binmat(c("000", "100", "101", "111"))
#> a b c
#> [1,] 0 0 0
#> [2,] 1 0 0
#> [3,] 1 0 1
#> [4,] 1 1 1
as.binmat(set(set(), set("a"), set("a", "c"), set("a", "b", "c")))
#> a b c
#> [1,] 0 0 0
#> [2,] 1 0 0
#> [3,] 1 0 1
#> [4,] 1 1 1
as.binmat(c("000", "100", "101", "111"), as.logical = TRUE)
#> a b c
#> [1,] FALSE FALSE FALSE
#> [2,] TRUE FALSE FALSE
#> [3,] TRUE FALSE TRUE
#> [4,] TRUE TRUE TRUE
## Subset relation incidence matrix
is.subset(K)
#> >
#> < 00000 10000 01000 11000 11100 11010 11110 11101 11111
#> 00000 TRUE TRUE TRUE TRUE TRUE TRUE TRUE TRUE TRUE
#> 10000 FALSE TRUE FALSE TRUE TRUE TRUE TRUE TRUE TRUE
#> 01000 FALSE FALSE TRUE TRUE TRUE TRUE TRUE TRUE TRUE
#> 11000 FALSE FALSE FALSE TRUE TRUE TRUE TRUE TRUE TRUE
#> 11100 FALSE FALSE FALSE FALSE TRUE FALSE TRUE TRUE TRUE
#> 11010 FALSE FALSE FALSE FALSE FALSE TRUE TRUE FALSE TRUE
#> 11110 FALSE FALSE FALSE FALSE FALSE FALSE TRUE FALSE TRUE
#> 11101 FALSE FALSE FALSE FALSE FALSE FALSE FALSE TRUE TRUE
#> 11111 FALSE FALSE FALSE FALSE FALSE FALSE FALSE FALSE TRUE
## Plotting the knowledge structure
if(requireNamespace("relations") &&
requireNamespace("Rgraphviz")) {
rownames(K) <- as.pattern(K, useNames = TRUE)
plot(relations::as.relation(is.subset(K)), main = "")
}
#> Loading required namespace: relations
#> Loading required namespace: Rgraphviz